在 URP 中实现兼容 HDR 输出的自定义叠加
此页面演示如何创建一个可脚本化渲染功能,该功能执行以下操作
- 将一个摄像机场景中创建特定视点的图像的组件。输出绘制到屏幕上或捕获为纹理。 更多信息
请参阅 术语表的输出合成到另一个摄像机上。 - 应用色调映射将图像的 HDR 值重新映射到适合在屏幕上显示的范围内的过程。 更多信息
请参阅 术语表,使自定义叠加与HDR高动态范围
请参阅 术语表输出的效果保持一致。
这包括根据帧顺序应用色调映射的着色器在 GPU 上运行的程序。 更多信息
请参阅 术语表。
有关更多信息,请参阅可脚本化渲染功能简介和可脚本化渲染通道简介。
此示例分为以下部分
- 先决条件
- 设置场景
- 创建自定义叠加渲染通道
- 实现 RecordRenderGraph 方法
- 创建自定义叠加渲染功能
- 创建自定义叠加着色器
- 完成自定义叠加
- 完整的代码示例
- 自定义叠加渲染通道代码
- 自定义叠加渲染功能代码
- 自定义叠加着色器代码
先决条件
此示例假设以下内容
- Unity 项目使用 URP 作为活动渲染管线一系列操作,这些操作获取场景的内容并在屏幕上显示它们。Unity 允许您从预构建的渲染管线中选择,或编写自己的渲染管线。 更多信息
请参阅 术语表。 - 该项目已设置为使用以下设置进行 HDR 渲染
- 活动 URP 资源的分级模式设置为高动态范围。
- 活动 URP 资源已启用HDR。
- 在项目设置大量设置的集合,允许您配置项目的物理、音频、网络、图形、输入以及许多其他方面的行为。 更多信息
请参阅 术语表中已启用HDR 输出。
设置场景
为了使示例正常工作,您必须首先设置一个示例场景场景包含游戏环境和菜单。可以将每个唯一的场景文件视为一个唯一的关卡。在每个场景中,您放置环境、障碍物和装饰,基本上是分段设计和构建游戏。 更多信息
请参阅 术语表,如以下说明所示。
创建一个立方体游戏对象Unity 场景中的基本对象,可以表示角色、道具、场景、摄像机、路径点等。游戏对象的函数由附加到它的组件定义。 更多信息
请参阅 术语表,并将其位置设置为场景中的原点(X:0,Y:0,Z:0)。调整
主摄像机,使立方体清晰可见。创建一个新的摄像机并将其命名为叠加摄像机。
将叠加摄像机放置在
主摄像机的右侧,并对其进行对齐,使立方体清晰可见。在检查器Unity 窗口,显示有关当前选定的游戏对象、资源或项目设置的信息,允许您检查和编辑值。 更多信息
请参阅 术语表窗口中,将叠加摄像机的背景类型属性设置为纯色。将叠加摄像机背景的颜色设置为透明黑色,RGBA 值为
0, 0, 0, 0。-
创建一个渲染纹理并将其命名为OverlayRenderTexture。要创建渲染纹理,请转到资源>创建>渲染>渲染纹理。
注意:为了获得更好的 HDR 精度,请对渲染纹理格式使用带符号浮点格式。为此,选择渲染纹理,然后在检查器窗口中将颜色格式更改为以
_SFLOAT结尾的格式。 将叠加渲染纹理分配给叠加摄像机的输出纹理属性。为此,在检查器中打开
叠加摄像机,然后转到输出>输出纹理,并从资源列表中选择OverlayRenderTexture。为叠加摄像机创建一个新的通用渲染器资源,并将其命名为OverlayRenderer。为此,请转到资源>创建>渲染>URP 通用渲染器。
选择活动 URP 资源,然后在检查器窗口中转到渲染>渲染器列表>+。选择OverlayRenderer。这会将叠加渲染器添加到渲染器列表中。
选择叠加摄像机,然后在检查器窗口中转到渲染>渲染器。选择OverlayRenderer。这会将叠加摄像机设置为使用叠加渲染器。
现在,场景已准备好使用可脚本化渲染功能创建自定义叠加。
创建自定义叠加渲染通道
要创建与 HDR 输出兼容的自定义叠加,必须使用可脚本化渲染通道来创建叠加。HDR 输出在后期处理在图像显示在屏幕上之前应用滤镜和效果来改进产品视觉效果的过程。例如,您可以使用后期处理效果来模拟物理相机和胶片属性,例如 Bloom 和景深。 更多信息 后期处理, 后处理, 后处理
请参阅 术语表期间将色调映射应用于主摄像机的输出。因此,主摄像机和叠加摄像机的输出具有不同的色调映射。然后,此渲染通道在后期处理之后发生,以将色调映射应用于叠加摄像机的输出。
要为此示例创建渲染通道,请使用以下步骤
创建一个 C# 脚本并将其命名为
CustomOverlayRenderPass。在脚本中,删除 Unity 在
CustomOverlayRenderPass类中插入的代码。-
添加以下
using指令。using UnityEngine; using UnityEngine.Rendering; using UnityEngine.Rendering.Universal; using UnityEngine.Rendering.RenderGraphModule; -
创建一个新的
CustomOverlayRenderPass类,该类继承自ScriptableRenderPass类,并具有属性[SupportedOnRenderer(typeof(UniversalRendererData) -->。[SupportedOnRenderer(typeof(UniversalRendererData))] --> public class CustomOverlayRenderPass : ScriptableRenderPass { } -
添加属性
Material passMaterial和RTHandle passOverlayTexture到渲染通道,如下所示。[SupportedOnRenderer(typeof(UniversalRendererData))] --> public class CustomOverlayRenderPass : ScriptableRenderPass { Material passMaterial; RTHandle overlayTextureHandle; } -
创建一个构造方法,该方法将材质作为参数并将其分配给
passMaterial。此方法还为渲染通道创建概要分析采样器,并将其设置为在AfterRenderingPostProcessing事件中运行。public CustomOverlayRenderPass(Material material) { passMaterial = material; profilingSampler = new ProfilingSampler(nameof(CustomOverlayRenderPass)); renderPassEvent = RenderPassEvent.AfterRenderingPostProcessing; } -
为渲染通道添加一个
Setup方法。使用此方法和参数从叠加纹理创建RTHandle,如下所示。使用RTHandle允许RenderPassAPI 与叠加渲染纹理一种特殊的纹理类型,在运行时创建和更新。要使用它们,首先创建一个新的渲染纹理,并指定一个摄像机渲染到其中。然后,您可以像使用普通纹理一样在材质中使用渲染纹理。 更多信息
请参阅 术语表进行交互。public void Setup(Texture overlayTex) { if (overlayTextureHandle != overlayTex) { overlayTextureHandle?.Release(); overlayTextureHandle = RTHandles.Alloc(overlayTex); } } -
实现
Dispose方法以在销毁渲染通道时释放叠加纹理。public void Dispose() { overlayTextureHandle?.Release(); } -
创建两个结构体,一个名为
CopyData,另一个名为PassData,其中包含如下所示的属性。这些结构体保存 URP 实现渲染通道所需的关键属性。struct CopyData { public TextureHandle source; } struct PassData { public TextureHandle source; public TextureHandle overlayTexture; public TextureHandle internalLut; public Vector4 lutParams; public Material material; } -
添加
RecordRenderGraph方法,如下所示。public override void RecordRenderGraph(RenderGraph renderGraph, ContextContainer frameData) { }
实现 RecordRenderGraph 方法
在CustomOverlayRenderPass类的RecordRenderGraph方法中添加以下步骤中的代码。
-
从帧数据中获取后期处理、资源和摄像机数据。
UniversalPostProcessingData postProcessingData = frameData.Get<UniversalPostProcessingData>(); UniversalResourceData resourceData = frameData.Get<UniversalResourceData>(); UniversalCameraData cameraData = frameData.Get<UniversalCameraData>(); -
从资源数据中获取活动颜色纹理。
TextureHandle activeCameraColor = resourceData.activeColorTexture; -
创建一个纹理来存储活动摄像机颜色目标。
RenderTextureDescriptor colorCopyDescriptor = cameraData.cameraTargetDescriptor; colorCopyDescriptor.depthBufferBits = (int) DepthBits.None; TextureHandle copiedColor = UniversalRenderer.CreateRenderGraphTexture(renderGraph, colorCopyDescriptor, "_CustomCameraColorCopy", false); -
创建一个
RasterRenderPass将活动摄像机颜色目标复制到纹理中。该副本将用于处理混合。using (var builder = renderGraph.AddRasterRenderPass<CopyData>("Custom Overlay Render Pass - Copy Camera", out var passData)) { passData.source = activeCameraColor; builder.UseTexture(passData.source, AccessFlags.Read); builder.SetRenderAttachment(copiedColor, 0, AccessFlags.WriteAll); builder.SetRenderFunc((CopyData data, RasterGraphContext context) => { Blitter.BlitTexture(context.cmd, data.source, new Vector4(1, 1, 0, 0), 0.0f, false); }); } -
创建另一个
RasterRenderPass使用自定义材质将叠加纹理复制到活动摄像机颜色目标。这是您在本指南的这一部分中添加的其余代码的容器。using (var builder = renderGraph.AddRasterRenderPass<PassData>("Custom Overlay Render Pass - Blit Overlay", out var passData)) { } -
设置渲染通道需要blit“位块传输”的简称。blit 操作是从内存中的一个位置到另一个位置传输数据块的过程。
请参阅 术语表叠加纹理的属性,如下所示。using (var builder = renderGraph.AddRasterRenderPass<PassData>("Custom Overlay Render Pass - Blit Overlay", out var passData)) { passData.material = passMaterial; builder.SetRenderAttachment(activeCameraColor, 0, AccessFlags.Write); passData.source = copiedColor; builder.UseTexture(passData.source, AccessFlags.Read); } -
将纹理导入渲染图系统,然后将纹理设置为输入。
passData.overlayTexture = renderGraph.ImportTexture(passOverlayTexture); builder.UseTexture(passData.overlayTexture, AccessFlags.Read); -
检查后期处理和 HDR 颜色分级。如果配置对于 HDR 输出正确,则将 HDR 使用的内部颜色 LUT 纹理设置为输入,并将参数传递给着色器。
if (postProcessingData.gradingMode == ColorGradingMode.HighDynamicRange && cameraData.postProcessEnabled) { passData.internalLut = resourceData.internalColorLut; builder.UseTexture(passData.internalLut, AccessFlags.Read); int lutHeight = postProcessingData.lutSize; int lutWidth = lutHeight * lutHeight; float postExposure = 1.0f; ColorAdjustments colorAdjustments = VolumeManager.instance.stack.GetComponent<ColorAdjustments>(); if (colorAdjustments != null) { postExposure = Mathf.Pow(2.0f, colorAdjustments.postExposure.value); } passData.lutParams = new Vector4(1f / lutWidth, 1f / lutHeight, lutHeight - 1f, postExposure); }注意:如果禁用后期处理,则 HDR 颜色转换将在此渲染通道之后应用,摄像机输出的预期颜色空间为默认的 Rec709。此示例中的代码在此处使用
if语句来防止此渲染通道在应用 HDR 之前更改叠加摄像机的输出。 -
在着色器上设置一个关键字以启用色调映射,并添加一个命令将叠加纹理 blit 到活动摄像机颜色目标。
builder.SetRenderFunc((PassData data, RasterGraphContext context) => { data.material.SetTexture("_OverlayTexture", data.overlayTexture); bool tonemappingActive = data.internalLut.IsValid(); CoreUtils.SetKeyword(data.material, "TONEMAPPING", tonemappingActive); if (tonemappingActive) { data.material.SetTexture("_InternalLut", data.internalLut); data.material.SetVector("_InternalLut_Params", data.lutParams); } Blitter.BlitTexture(context.cmd, data.source, new Vector4(1, 1, 0, 0), data.material, 0); });
这完成了CustomOverlayRenderPass脚本,准备让可脚本化渲染功能将其添加到渲染器中。
有关本节的完整代码,请参阅自定义叠加渲染通道代码。
创建自定义叠加可脚本化渲染功能
要将CustomOverlayRenderPass添加到渲染器,必须使用以下步骤创建一个可脚本化渲染功能。
创建一个 C# 脚本并将其命名为
CustomOverlayRendererFeature。在脚本中,移除 Unity 在
CustomOverlayRendererFeature类中插入的代码。-
添加以下
using指令。using UnityEngine; using UnityEngine.Rendering; using UnityEngine.Rendering.Universal; -
设置一个新的
CustomOverlayRendererFeature类,该类继承自ScriptableRendererFeature类。public class CustomOverlayRendererFeature : ScriptableRendererFeature { } -
添加以下属性以包含渲染通道所需的资源和数据。
public class CustomOverlayRendererFeature : ScriptableRendererFeature { public Shader hdrShader; public RenderTexture passOverlayTexture; Material passMaterial; CustomOverlayRenderPass overlayRenderPass = null; } -
创建
AddRenderPasses方法,并使用它仅在游戏视图中以及相机堆栈中的最后一个相机上应用叠加。public override void AddRenderPasses(ScriptableRenderer renderer, ref RenderingData renderingData) { if (renderingData.cameraData.cameraType != CameraType.Game || !renderingData.cameraData.resolveFinalTarget) return; } -
在
if语句之后,将叠加纹理传递给叠加渲染通道并将其排队。public override void AddRenderPasses(ScriptableRenderer renderer, ref RenderingData renderingData) { if (renderingData.cameraData.cameraType != CameraType.Game || !renderingData.cameraData.resolveFinalTarget) return; overlayRenderPass.Setup(passOverlayTexture); renderer.EnqueuePass(overlayRenderPass); } -
添加
Create方法并创建一个CustomOverlayRenderPass的实例,该实例使用一个新的材质,该材质使用hdrShader。public override void Create() { passMaterial = CoreUtils.CreateEngineMaterial(hdrShader); overlayRenderPass = new CustomOverlayRenderPass(passMaterial); } -
实现
Dispose方法,以便在渲染功能应用渲染通道后释放其创建的资源。protected override void Dispose(bool disposing) { CoreUtils.Destroy(passMaterial); overlayRenderPass.Dispose(); }
有关本节的完整代码,请参阅 自定义叠加可脚本化渲染功能代码。
创建自定义叠加着色器
CustomOverlayRendererFeature 创建的材质需要一个自定义着色器来处理叠加和 HDR 输出更改。以下步骤演示如何创建一个能够实现此目的的着色器。
创建一个新的着色器并将其命名为
CustomOverlayBlit。-
删除 Unity 自动生成的着色器代码,并设置如下所示的着色器轮廓。
Shader "Custom/CustomOverlayBlit" { SubShader { Tags{ "RenderPipeline" = "UniversalPipeline" } Pass { ZWrite Off ZTest Always Blend Off Cull Off HLSLPROGRAM #pragma target 2.0 #pragma editor_sync_compilation #pragma vertex Vert #pragma fragment Frag #pragma multi_compile_local_fragment _ TONEMAPPING #include "Packages/com.unity.render-pipelines.universal/ShaderLibrary/Core.hlsl" #include "Packages/com.unity.render-pipelines.core/Runtime/Utilities/Blit.hlsl" #include "Packages/com.unity.render-pipelines.core/ShaderLibrary/Color.hlsl" TEXTURE2D(_InternalLut); TEXTURE2D_X(_OverlayTexture); float4 _InternalLut_Params; #define LutParams _InternalLut_Params.xyz #define PostExposure _InternalLut_Params.w ENDHLSL } } } 创建一个名为
ApplyTonemapping且返回类型为half3的方法。此方法应具有以下参数:half3 input、TEXTURE2D_PARAM(lutTex, lutSampler)、float3 lutParams、float exposure。-
在
ApplyTonemapping方法中,将input乘以exposure值,然后saturate修改后的input。half3 ApplyTonemapping(half3 input, TEXTURE2D_PARAM(lutTex, lutSampler), float3 lutParams, float exposure) { input *= exposure; float3 inputLutSpace = saturate(LinearToLogC(input)); } -
使用
ApplyLut2D应用色调映射更改并返回结果。half3 ApplyTonemapping(half3 input, TEXTURE2D_PARAM(lutTex, lutSampler), float3 lutParams, float exposure) { input *= exposure; float3 inputLutSpace = saturate(LinearToLogC(input)); return ApplyLut2D(TEXTURE2D_ARGS(lutTex, lutSampler), inputLutSpace, lutParams); } -
创建一个标准的
Frag方法,如下所示。将此方法放在HLSLPROGRAM内,但在ApplyTonemapping方法之后。half4 Frag(Varyings input) : SV_Target { } -
在
Frag方法中,检索原始相机颜色和叠加颜色。half4 Frag(Varyings input) : SV_Target { half4 color = FragBlit(input, sampler_LinearClamp); half4 overlay = SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D_X(_OverlayTexture, sampler_LinearClamp, input.texcoord); } -
创建一个
if语句以检查着色器是否应该应用色调映射。如果着色器应该应用色调映射,则使用ApplyTonemapping方法将其应用于叠加。half4 Frag(Varyings input) : SV_Target { half4 color = FragBlit(input, sampler_LinearClamp); half4 overlay = SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D_X(_OverlayTexture, sampler_LinearClamp, input.texcoord); #if TONEMAPPING overlay.rgb = ApplyTonemapping(overlay.rgb, TEXTURE2D_ARGS(_InternalLut, sampler_LinearClamp), LutParams, PostExposure); #endif } -
将叠加与原始相机颜色混合并返回结果。
half4 Frag(Varyings input) : SV_Target { half4 color = FragBlit(input, sampler_LinearClamp); half4 overlay = SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D_X(_OverlayTexture, sampler_LinearClamp, input.texcoord); #if TONEMAPPING overlay.rgb = ApplyTonemapping(overlay.rgb, TEXTURE2D_ARGS(_InternalLut, sampler_LinearClamp), LutParams, PostExposure); #endif color.rgb = color.rgb * (1.0 - overlay.a) + overlay.rgb * overlay.a; return color; }
着色器现在已完成并准备在 CustomOverlayRenderPass 和 CustomOverlayRendererFeature 脚本一段代码,允许您创建自己的组件、触发游戏事件、随时间修改组件属性并以任何您喜欢的方式响应用户输入。 更多信息
参见 词汇表中使用。
要查看本节的完整代码,请参阅 自定义叠加着色器代码。
完成自定义叠加
要完成自定义叠加,必须设置您创建的脚本,以将其效果应用于场景中的渲染器。以下步骤演示如何执行此操作。
- 查找并选择活动 URP 资源使用的主渲染器。
- 在检查器窗口中,选择添加渲染功能 > 自定义叠加渲染功能 以添加
CustomOverlayRendererFeature脚本。 - 将
CustomOverlayBlit着色器分配给自定义叠加可脚本化渲染功能的着色器属性。 - 将
OverlayRenderTexture分配给自定义叠加可脚本化渲染功能的叠加纹理属性。
自定义叠加现在已完成,应在播放模式下显示在主相机输出的顶部。叠加应以与主相机输出相同的方式进行色调映射,没有明显的差异。这应该类似于下面的屏幕截图。
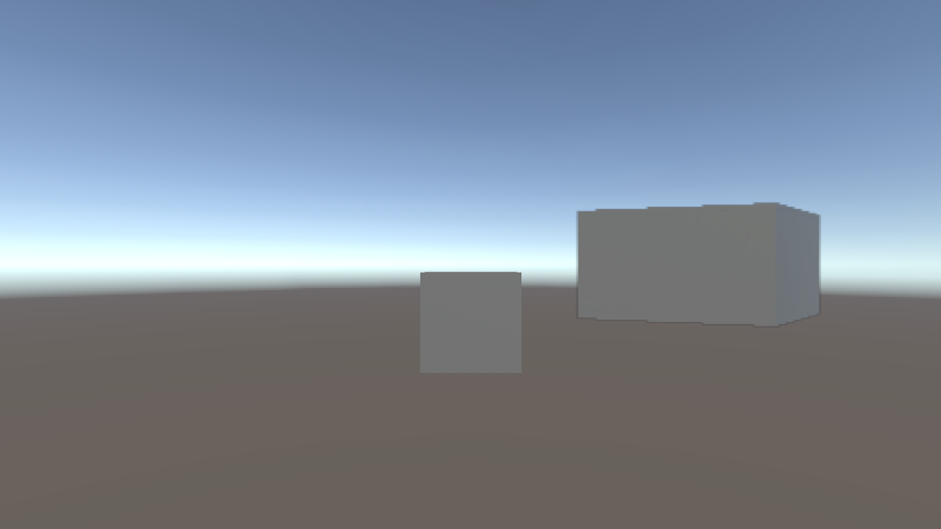
游戏视图中间的立方体,以及另一个角度的立方体作为叠加,色调映射以匹配 HDR 输出。
注意:最终结果可能会因叠加相机的放置而异。
完整的代码示例
自定义叠加渲染通道代码
以下是示例中可脚本化渲染通道的完整代码示例。
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.Rendering;
using UnityEngine.Rendering.Universal;
using UnityEngine.Rendering.RenderGraphModule;
[SupportedOnRenderer(typeof(UniversalRendererData))] -->
public class CustomOverlayRenderPass : ScriptableRenderPass
{
Material passMaterial;
RTHandle overlayTextureHandle;
public CustomOverlayRenderPass(Material material)
{
passMaterial = material;
profilingSampler = new ProfilingSampler(nameof(CustomOverlayRenderPass));
// The render pass is executed after post processing, so the main camera target has been tonemapped but not the overlay texture
renderPassEvent = RenderPassEvent.AfterRenderingPostProcessing;
}
public void Setup(Texture overlayTex)
{
//Create an RTHandle from the overlay texture, to import it into the render graph system
if (overlayTextureHandle != overlayTex)
{
overlayTextureHandle?.Release();
overlayTextureHandle = RTHandles.Alloc(overlayTex);
}
}
public void Dispose()
{
overlayTextureHandle?.Release();
}
class CopyData
{
public TextureHandle source;
}
class PassData
{
public TextureHandle source;
public TextureHandle overlayTexture;
public TextureHandle internalLut;
public Vector4 lutParams;
public Material material;
}
public override void RecordRenderGraph(RenderGraph renderGraph, ContextContainer frameData)
{
UniversalPostProcessingData postProcessingData = frameData.Get<UniversalPostProcessingData>();
UniversalResourceData resourceData = frameData.Get<UniversalResourceData>();
UniversalCameraData cameraData = frameData.Get<UniversalCameraData>();
TextureHandle activeCameraColor = resourceData.activeColorTexture;
// Create a texture to copy the active camera color target into
RenderTextureDescriptor colorCopyDescriptor = cameraData.cameraTargetDescriptor;
colorCopyDescriptor.depthBufferBits = (int) DepthBits.None;
TextureHandle copiedColor = UniversalRenderer.CreateRenderGraphTexture(renderGraph, colorCopyDescriptor, "_CustomCameraColorCopy", false);
// Copy the active camera color target into the texture
using (var builder = renderGraph.AddRasterRenderPass<CopyData>("Custom Overlay Render Pass - Copy Camera", out var passData))
{
passData.source = activeCameraColor;
builder.UseTexture(passData.source, AccessFlags.Read);
builder.SetRenderAttachment(copiedColor, 0, AccessFlags.WriteAll);
builder.SetRenderFunc((CopyData data, RasterGraphContext context) =>
{
Blitter.BlitTexture(context.cmd, data.source, new Vector4(1, 1, 0, 0), 0.0f, false);
});
}
using (var builder = renderGraph.AddRasterRenderPass<PassData>("Custom Overlay Render Pass - Blit Overlay", out var passData))
{
passData.material = passMaterial;
builder.SetRenderAttachment(activeCameraColor, 0, AccessFlags.Write);
passData.source = copiedColor;
builder.UseTexture(passData.source, AccessFlags.Read);
// Import the overlay texture that will be copied onto the camera color, and set it as an input
passData.overlayTexture = renderGraph.ImportTexture(overlayTextureHandle);
builder.UseTexture(passData.overlayTexture, AccessFlags.Read);
// If post-processing is enabled on the main camera, apply the tonemapping to the overlay texture as well
// If post processing is disabled, the HDR color conversion will be applied after this render pass and the expected colorspace for the cameras output is the default Rec709
if (postProcessingData.gradingMode == ColorGradingMode.HighDynamicRange && cameraData.postProcessEnabled)
{
// Import the internal color LUT texture used for HDR color grading and tonemapping
// This includes any HDR color conversion URP needs for the display, so the output of the camera is in the display's color gamut
passData.internalLut = resourceData.internalColorLut;
builder.UseTexture(passData.internalLut, AccessFlags.Read);
// Pass LUT parameters to the shader
int lutHeight = postProcessingData.lutSize;
int lutWidth = lutHeight * lutHeight;
float postExposure = 1.0f;
ColorAdjustments colorAdjustments = VolumeManager.instance.stack.GetComponent<ColorAdjustments>();
if (colorAdjustments != null)
{
postExposure = Mathf.Pow(2.0f, colorAdjustments.postExposure.value);
}
passData.lutParams = new Vector4(1f / lutWidth, 1f / lutHeight, lutHeight - 1f, postExposure);
}
builder.SetRenderFunc((PassData data, RasterGraphContext context) =>
{
// Pass parameters to the shader
data.material.SetTexture("_OverlayTexture", data.overlayTexture);
// Set a keyword on the shader to enable tonemapping
bool tonemappingActive = data.internalLut.IsValid();
CoreUtils.SetKeyword(data.material, "TONEMAPPING", tonemappingActive);
if (tonemappingActive)
{
data.material.SetTexture("_InternalLut", data.internalLut);
data.material.SetVector("_InternalLut_Params", data.lutParams);
}
// Blit the overlay texture onto the camera color
Blitter.BlitTexture(context.cmd, data.source, new Vector4(1, 1, 0, 0), data.material, 0);
});
}
}
}
自定义叠加可脚本化渲染功能代码
以下是示例中可脚本化渲染功能的完整代码示例。
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.Rendering;
using UnityEngine.Rendering.Universal;
public class CustomOverlayRendererFeature : ScriptableRendererFeature
{
public Shader hdrShader;
public RenderTexture passOverlayTexture;
Material passMaterial;
CustomOverlayRenderPass overlayRenderPass = null;
public override void AddRenderPasses(ScriptableRenderer renderer, ref RenderingData renderingData)
{
// Render the overlay onto the main camera during Game view rendering only, for the last camera in the camera stack
if (renderingData.cameraData.cameraType != CameraType.Game || !renderingData.cameraData.resolveFinalTarget)
return;
// Pass the overlay texture at runtime in case it changes
overlayRenderPass.Setup(passOverlayTexture);
// Enqueue the render pass to be executed
renderer.EnqueuePass(overlayRenderPass);
}
public override void Create()
{
// Create a blit material from the given shader
passMaterial = CoreUtils.CreateEngineMaterial(hdrShader);
// Create the render pass
overlayRenderPass = new CustomOverlayRenderPass(passMaterial);
}
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
// Destroy the render pass resources
CoreUtils.Destroy(passMaterial);
overlayRenderPass.Dispose();
}
}
自定义叠加着色器代码
以下是示例中着色器的完整代码示例。
Shader "Custom/CustomOverlayBlit"
{
SubShader
{
Tags{ "RenderPipeline" = "UniversalPipeline" }
Pass
{
ZWrite Off ZTest Always Blend Off Cull Off
HLSLPROGRAM
#pragma target 2.0
#pragma editor_sync_compilation
#pragma vertex Vert
#pragma fragment Frag
#pragma multi_compile_local_fragment _ TONEMAPPING
#include "Packages/com.unity.render-pipelines.universal/ShaderLibrary/Core.hlsl"
#include "Packages/com.unity.render-pipelines.core/Runtime/Utilities/Blit.hlsl"
#include "Packages/com.unity.render-pipelines.core/ShaderLibrary/Color.hlsl"
TEXTURE2D(_InternalLut);
TEXTURE2D_X(_OverlayTexture);
float4 _InternalLut_Params;
#define LutParams _InternalLut_Params.xyz
#define PostExposure _InternalLut_Params.w
half3 ApplyTonemapping(half3 input, TEXTURE2D_PARAM(lutTex, lutSampler), float3 lutParams, float exposure)
{
input *= exposure;
float3 inputLutSpace = saturate(LinearToLogC(input)); // LUT space is in LogC
return ApplyLut2D(TEXTURE2D_ARGS(lutTex, lutSampler), inputLutSpace, lutParams);
}
half4 Frag(Varyings input) : SV_Target
{
// Get the original camera color
half4 color = FragBlit(input, sampler_LinearClamp);
// Get the overlay color
half4 overlay = SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D_X(_OverlayTexture, sampler_LinearClamp, input.texcoord);
// Tonemap the overlay
#if TONEMAPPING
overlay.rgb = ApplyTonemapping(overlay.rgb, TEXTURE2D_ARGS(_InternalLut, sampler_LinearClamp), LutParams, PostExposure);
#endif
// Blend overlay and color
color.rgb = color.rgb * (1.0 - overlay.a) + overlay.rgb * overlay.a;
return color;
}
ENDHLSL
}
}
}